Edema disease
The Edema disease happens during the weaning period and it is characterized by a E. coli K88 (F4) or F18 producing a very strong vascular toxin inducing sudden death, edema and/or nervous signs.
Alternative names: E. coli, post-weaning diarrhea, Bowel edema
Information
Caused by certain E. coli serotypes that produce a very powerful toxin (Stx2e). The usual E. coli serotypes are K88 (F4) or F18. This toxin damages the small blood vessels walls, including the ones situated in the brain, and produce fluid accumulation or edema. The damage produced to the blood vessels in the brain produces characteristic nervous symptoms. The disease usually appears 1 to 4 weeks after weaning, reaching its peak 10 days after weaning.
Symptoms
Sows, lactating piglets and growers
- Not present.
Weaners
Sometimes the only visible sign is finding a good pig death.
Affected pigs show:
- Incoordination
- Pigs stop eating.
- In the last part of the disease pigs suffer from partial paralysis and fall down.
- Sometimes nervous signs are present.
- Diarrhea is not a typical symptom.
- Brain damage is irreversible and most of the pigs die.
- Face or eyelid edema are common.
- Acutely affected animals do not present fever, on the contrary, their temperature is low.
Causes / Contributing Factors
- Associated to weaning and diet changes.
- Contaminated barns.
Diagnosis
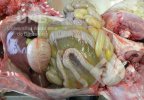
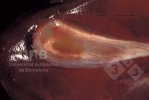
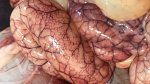
It is obtained from typical clinical signs, and the sudden presentation of the disease after farrowing; the necropsy, which shows edema (fluid in tissues) in the greater curvature of the stomach, spiral colon and eyelids; and the isolation of usually haemolytic E. coli serotypes that produce the Stx2 toxin from the anterior small intestine. Animals do not present fever.
Control/Prevention
When clinical signs are observed, it is too late and most of the affected pigs die. Treatments try to avoid the establishment of the organism, and reduce the infection load. General principles to control coliforms infections and post weaning diarrheas must be followed.
- Isolation of the organism and determination of the sensibility to antibiotics.
- Identify when the disease appears for the first time (for example 10 days after weaning) and medicate feed or water 3 to 5 days before.
- Use oral vaccines at weaning to prevent the disease.
Atlas of pathology
See images in the Altlas related to Edema disease