Ovarian cysts and uterine dilation - Atlas of swine pathology
Where: genitourinary system, female genitourinay tract
Possible causes: Other
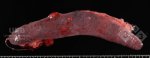
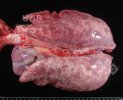
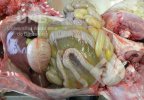
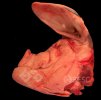
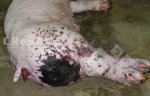
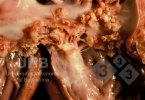
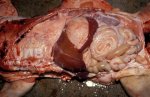
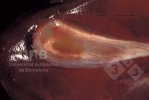
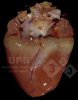
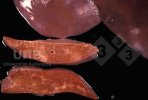
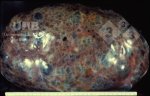
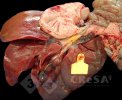
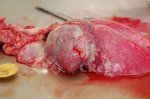
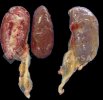
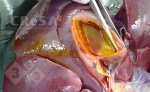
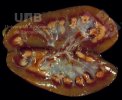
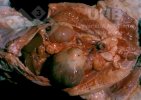
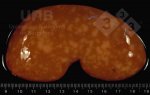
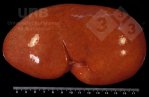
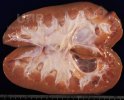
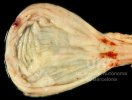
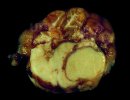
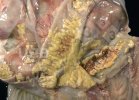
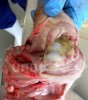
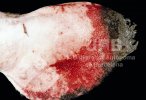
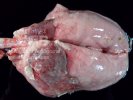
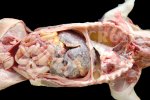
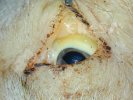
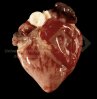
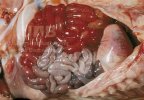
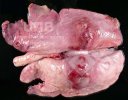
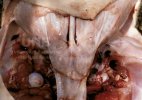
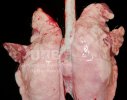
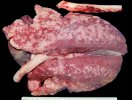
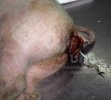
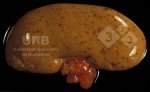
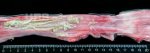
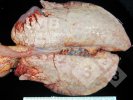
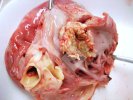
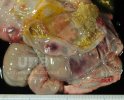
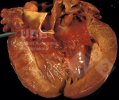
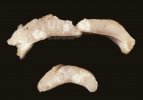
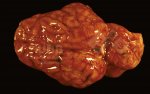
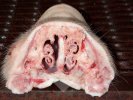
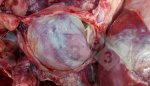
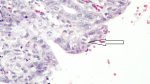
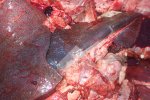
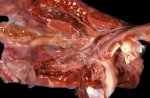
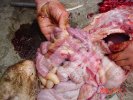
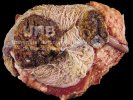
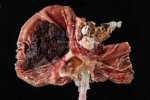
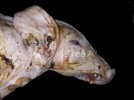
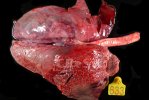
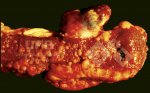
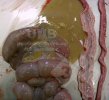
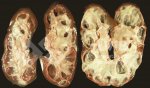
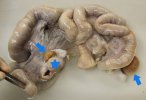
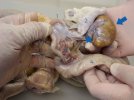
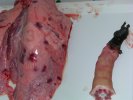
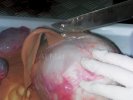
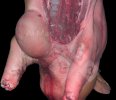
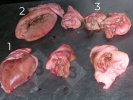
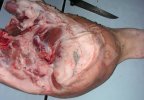
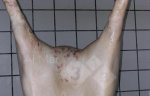
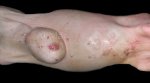
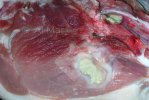
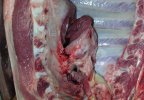
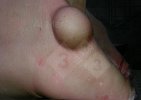
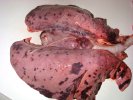
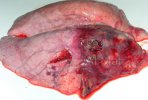
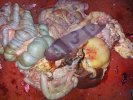
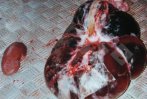
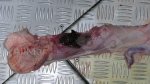
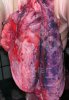
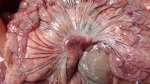
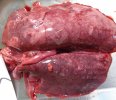
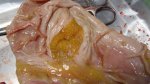
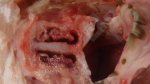
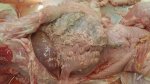
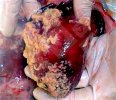
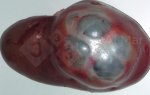
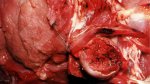
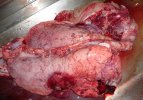
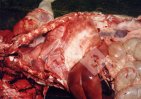
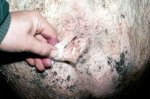
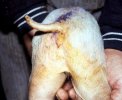
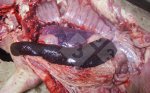
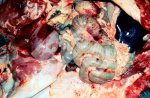
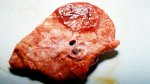
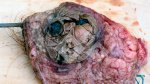
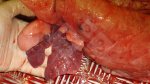
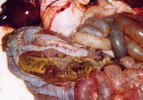
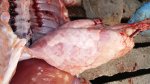
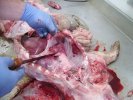
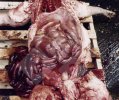
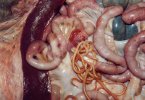
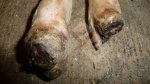
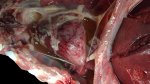
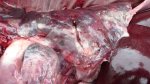
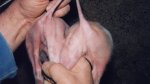
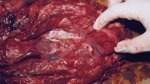
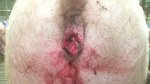
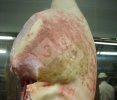
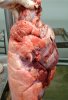
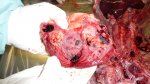
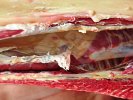
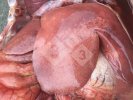
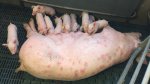
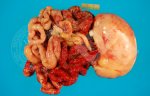
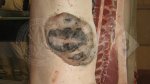
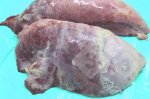
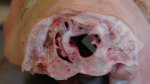
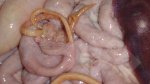
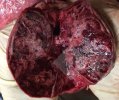
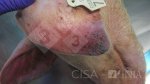
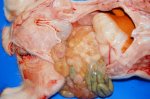
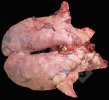
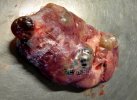
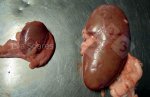
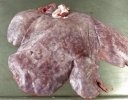
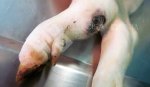
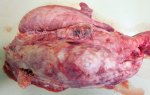
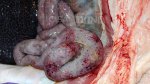
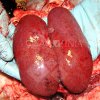
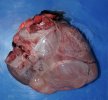
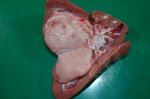
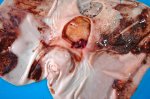
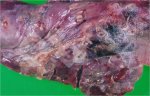
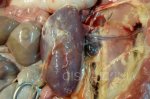
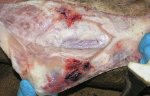
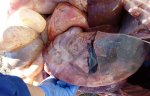
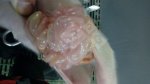
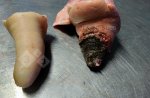
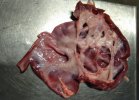
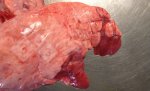
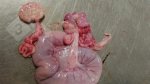
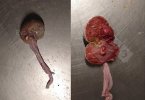
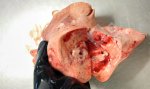
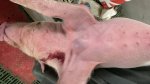
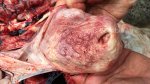
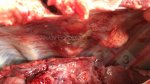
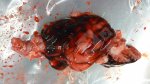
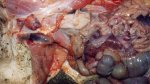
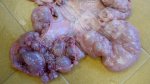
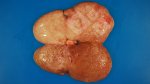
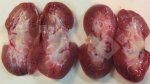
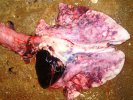
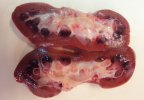
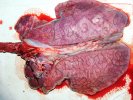
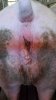
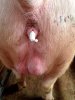
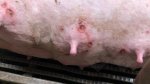
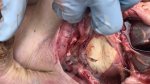
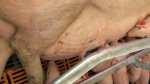
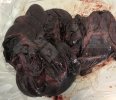
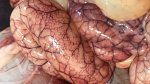
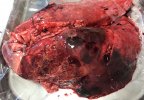
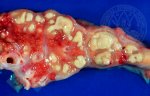
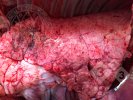
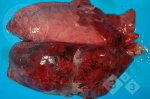
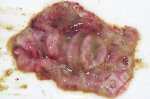
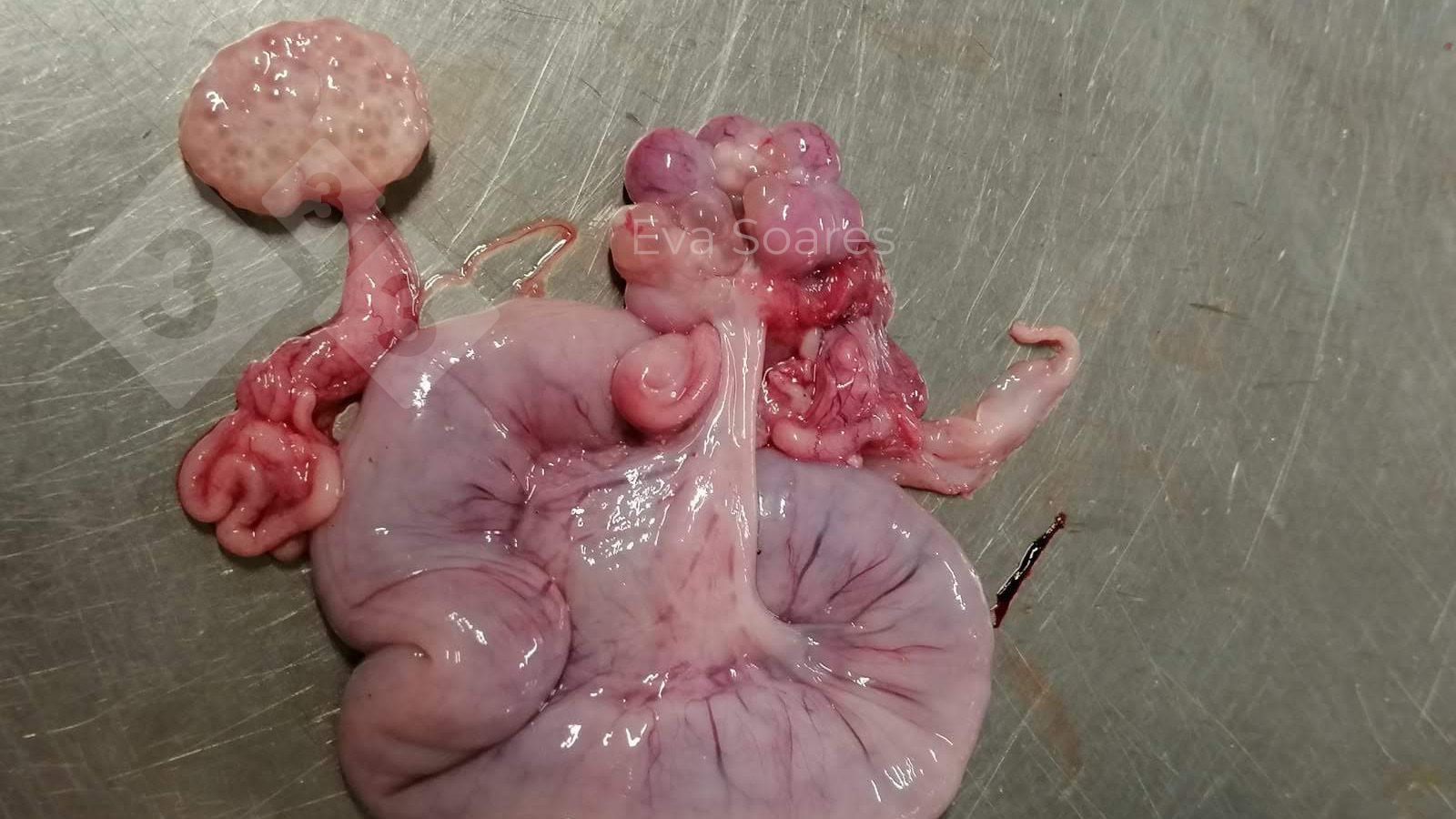
The ovary on the left side of the picture is normal, while the right-side ovary has an lesion compatible with ovarian cysts, which are the most commonly detected ovarian abnormality at the slaughterhouse. This type of lesion can be unilateral or bilateral. Follicular cysts can be simple, usually large, or multiple. Cysts can also be corpus luteum cysts, evolving from the previous ones and showing a partial luteinization of the follicular structure. There is a combined form called cystic ovarian degeneration associated with the simultaneous presence of cysts of different sizes which, in some publications, appear to be the predominant form of ovarian cysts in female pigs. If cystic changes in the ovaries are prolonged, the uterus often shows signs of progestogenic hyperplasia or enlargement of the clitoris.
Differential diagnosis: cistoadenoma, cyclic ovary in luteal phase or follicular phase.