Osteochondrosis - Atlas of swine pathology
Where: musculoskeletal system
Possible causes: OsteochondrosisOther
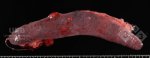
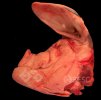
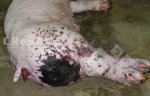
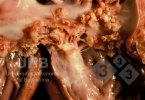
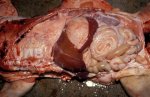
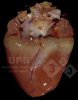
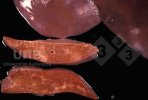
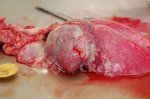
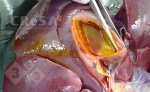
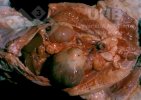
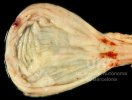
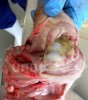
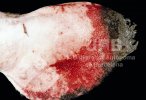
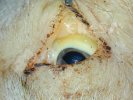
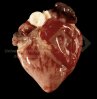
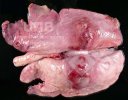
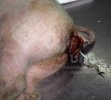
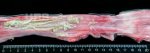
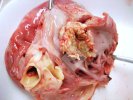
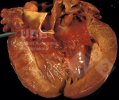
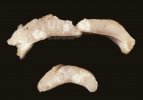
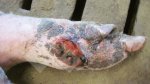
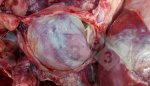
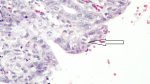
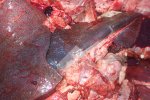
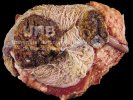
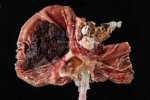
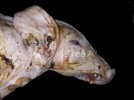
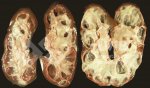
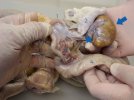
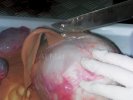
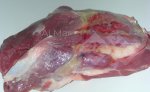
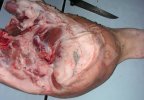
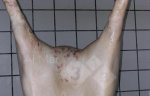
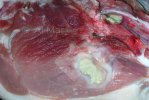
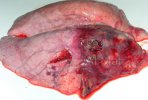
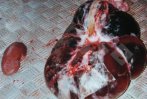
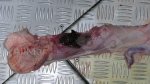
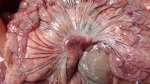
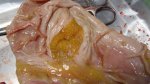
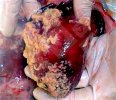
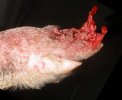
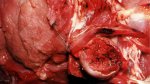
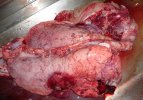
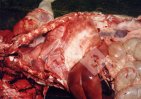
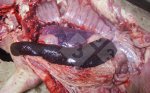
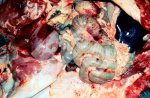
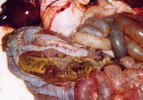
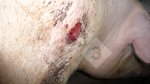
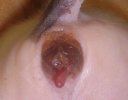
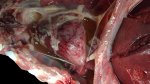
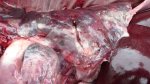
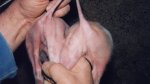
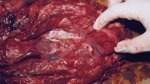
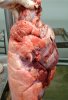
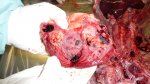
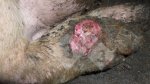
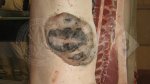
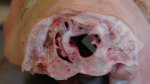
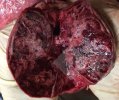
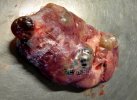
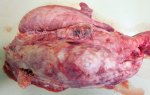
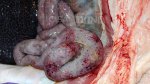
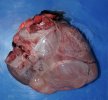
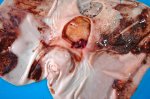
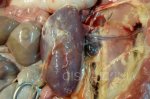
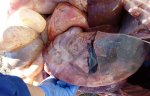
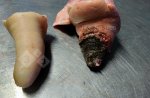
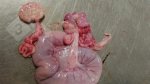
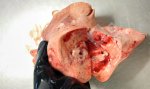
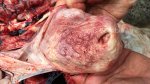
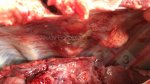
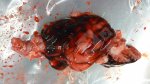
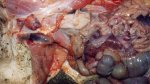
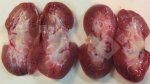
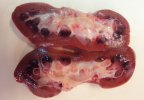
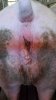
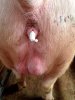
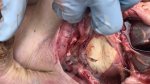
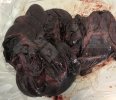
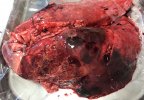
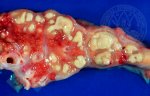
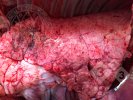
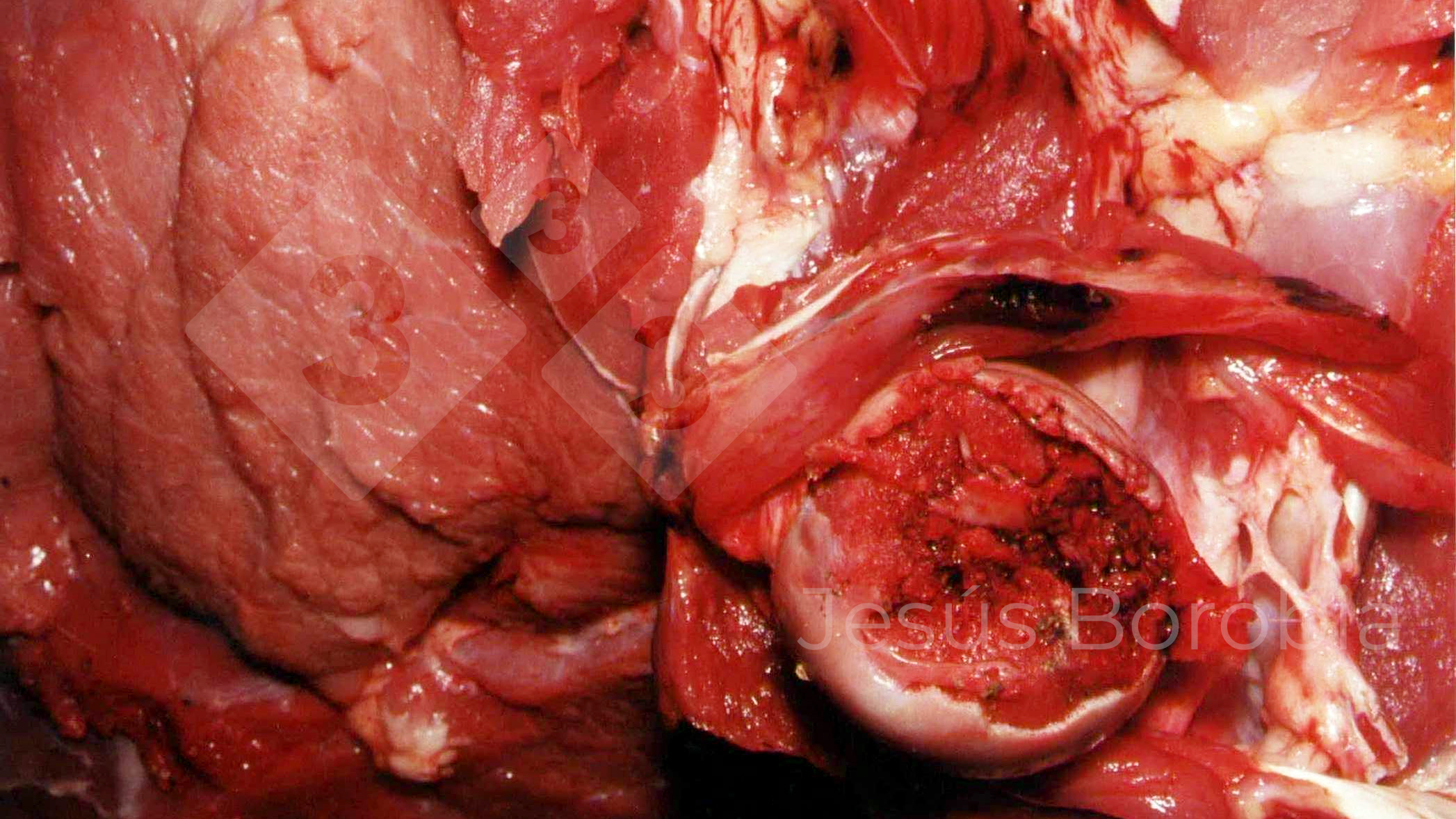
Severe erosion of the articular cartilage in the right humeral epiphysis.
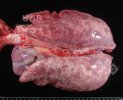
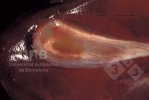
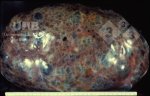
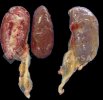
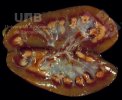
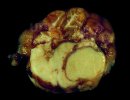
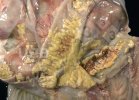
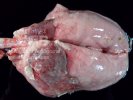
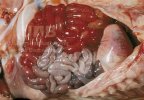
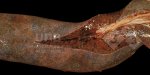
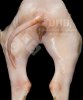
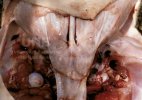
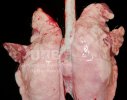
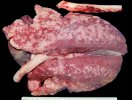
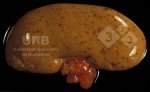
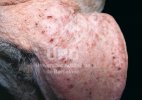
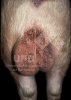
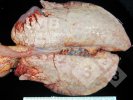
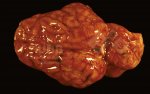
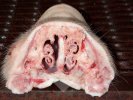
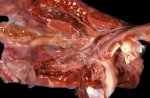
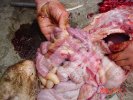
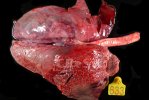
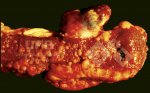
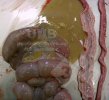
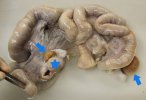
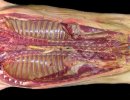
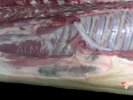
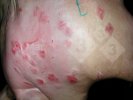
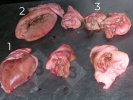
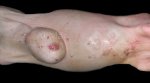
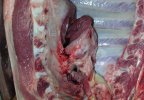
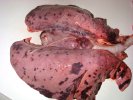
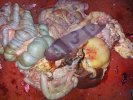
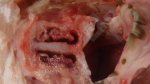
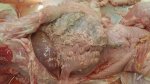
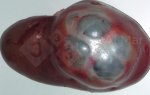
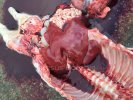
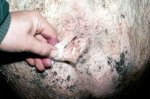
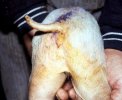
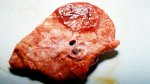
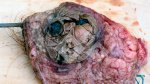
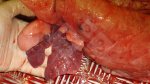
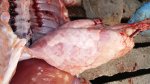
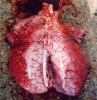
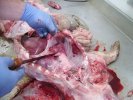
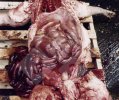
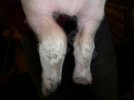
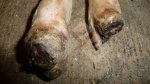
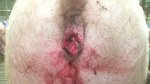
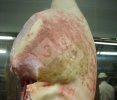
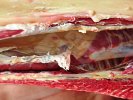
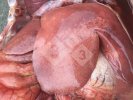
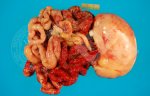
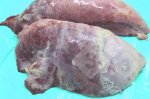
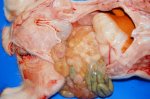
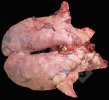
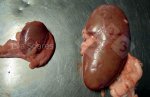
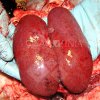
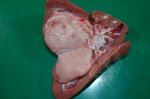
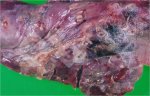
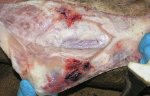
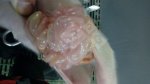
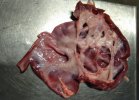
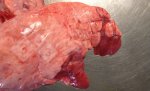
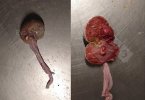
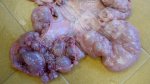
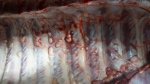
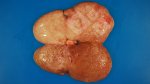
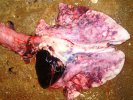
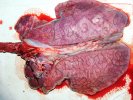
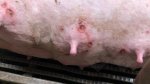
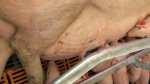
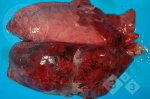
Osteochondrosis is common in the rapidly growing pig. It arises due to abnormal changes in the articular cartilage and the growth (epiphyseal) plates. Damage to the cartilage tends to be progressive and irreversible.
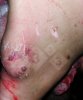
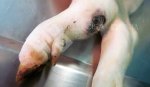
The aetiology of osteochondrosis (OCD) is mulifactorial: bad leg conformation is a predisposing factor. Trauma is also involved so slippery floors or overcrowding have a negative effect. Defects in vascular supply, and calcium /phosphorus supply or imbalance also have an effect in OCD.
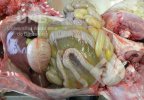
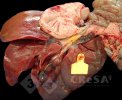
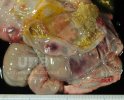
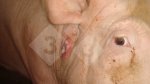
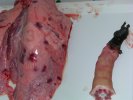
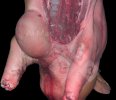
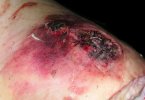
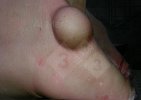
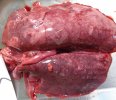
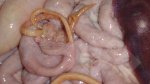
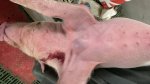
OCD can affect heavy finisher animals and gilts and may involve the femoral head. In older animals can cause caudal weakness and inability to stand and often occurs around farrowing time.