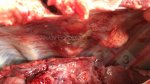
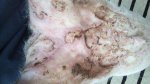
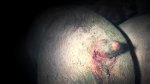
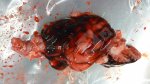
Dermatitis - Atlas of swine pathology
Where:
Possible causes: ErysipelaExudative EpidermitisMangePorcine circovirosisOther
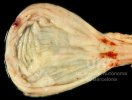
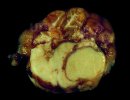
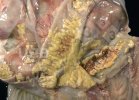
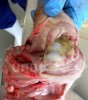
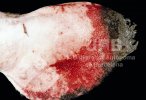
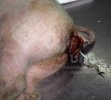
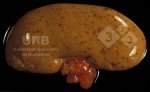
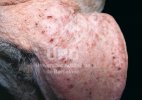
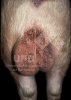
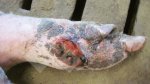
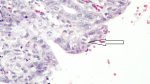
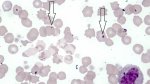
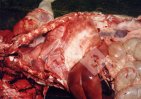
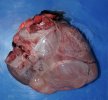
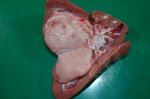
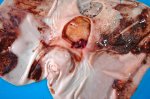
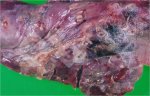
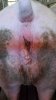
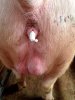
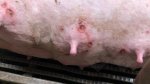
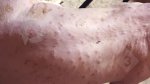
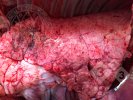
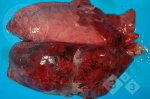
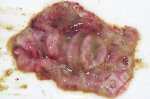
The causative agent is Erysipelothrix rhusiophathiae.
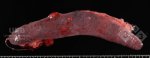
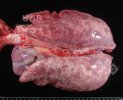
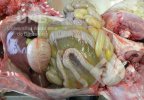
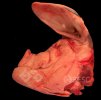
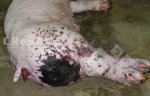
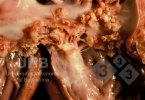
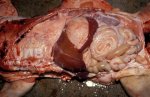
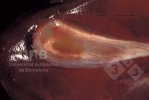
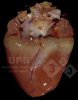
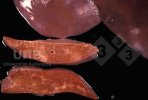
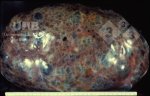
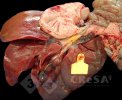
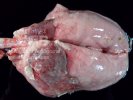
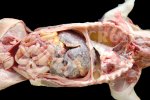
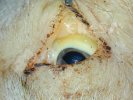
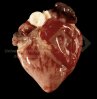
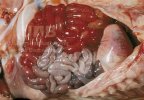
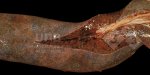
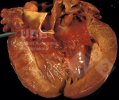
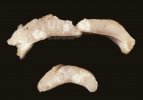
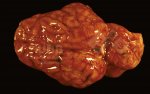
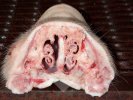
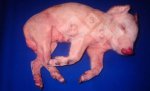
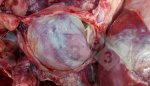
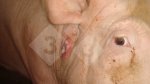
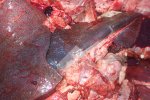
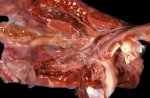
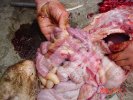
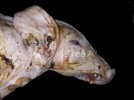
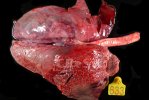
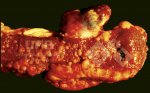
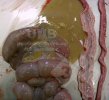
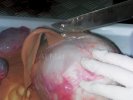
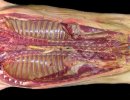
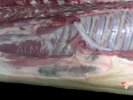
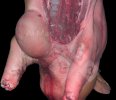
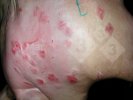
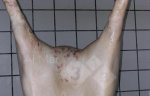
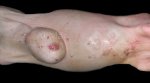
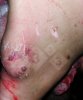
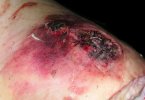
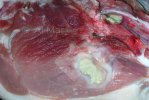
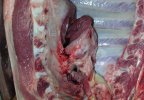
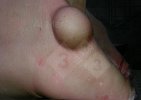
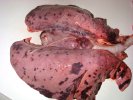
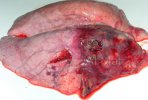
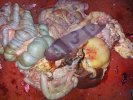
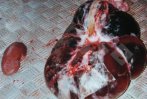
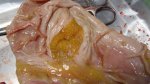
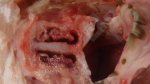
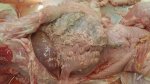
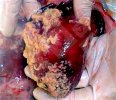
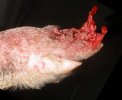
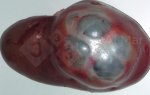
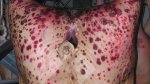
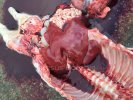
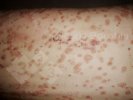
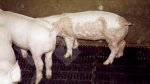
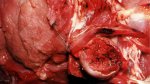
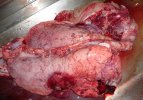
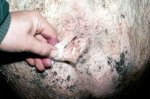
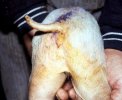
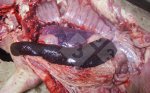
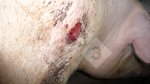
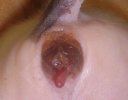
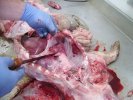
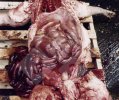
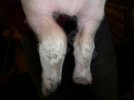
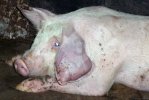
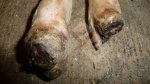
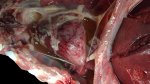
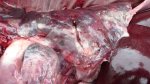
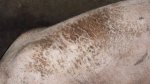
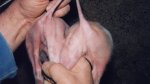
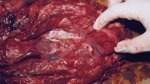
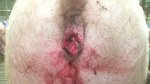
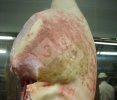
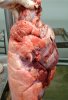
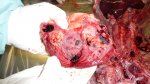
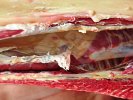
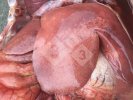
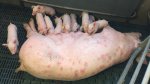
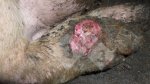
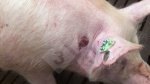
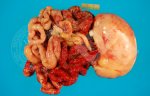
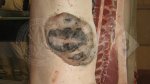
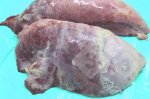
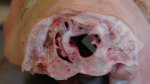
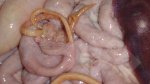
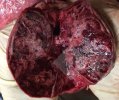
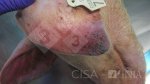
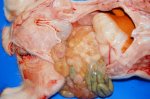
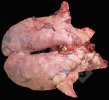
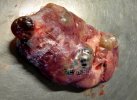
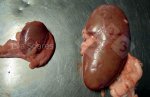
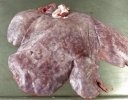
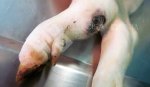
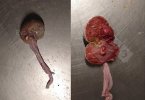
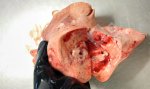
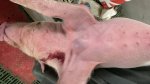
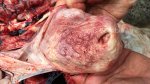
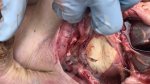
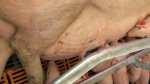
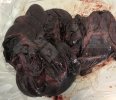
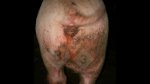
In gilts, fattening pigs and young boars, inappetence and high fever of 41.1-42.2°C is common and there may be flushing or blotching of the skin and ears. Affected animals are dull and reluctant to move. Diamond skin lesions occur within 48 hours of the onset of clinical signs and can be felt as raised patches along the back or neck but rapidly become purplish-red. Abortion may occur in sows, temporary infertility occurs in boars and served sows may return. Affected animals may recover completely, but the skin lesions may become necrotic (die), turn black and slough. The tips of the ears may also be lost. Arthritis may develop and cause lameness. The heart valves may develop lesions and give rise to a murmur. Sudden death or signs of congestive heart failure may occur later.
Injections of penicillin are used for the treatment of erysipelas and the response is normally rapid.