Cutaneous hyperaemia - Atlas of swine pathology

Where: skin and subcutaneous tissue
Possible causes: Other
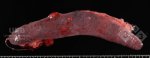
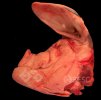
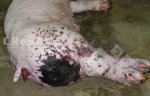
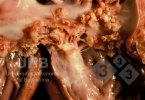
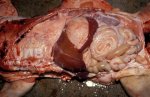
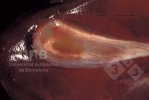
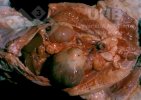
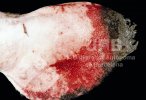
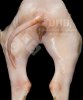
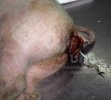
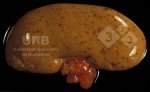
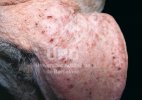
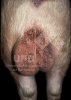
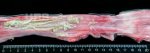
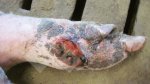
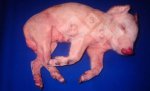
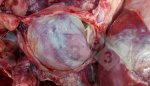
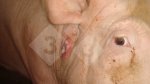
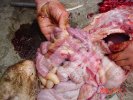
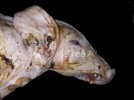
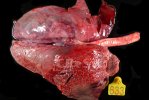
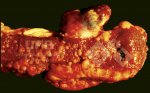
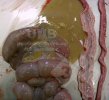
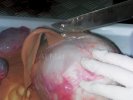
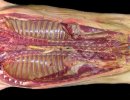
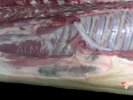
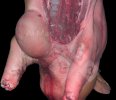
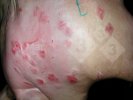
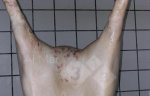
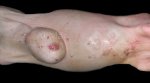
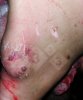
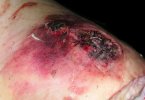
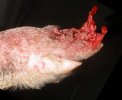
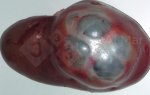
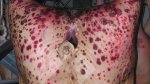
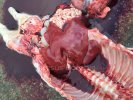
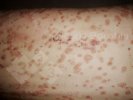
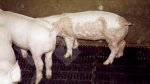
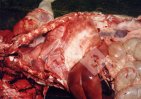
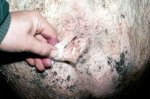
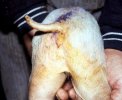
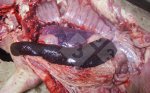
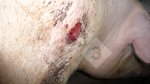
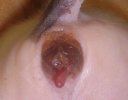
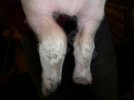
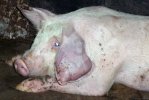
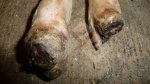
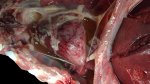
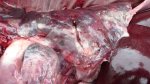
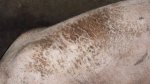
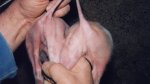
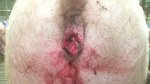
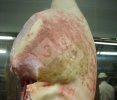
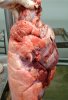
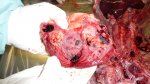
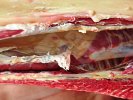
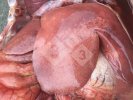
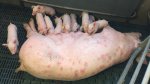
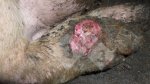
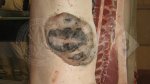
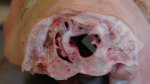
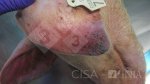
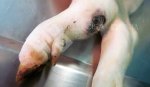
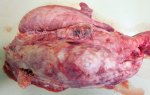
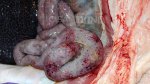
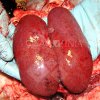
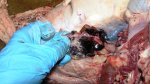
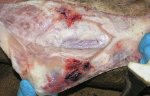
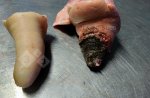
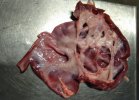
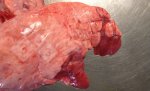
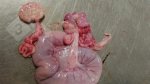
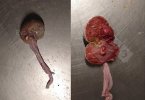
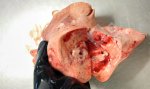
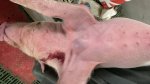
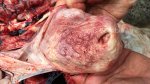
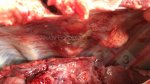
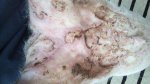
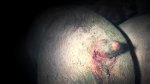
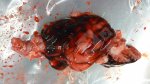
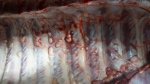
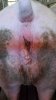
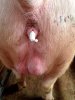
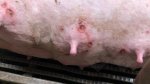
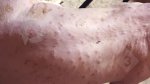
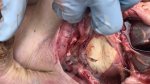
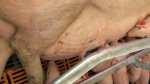
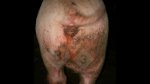
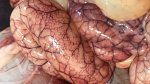
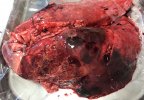
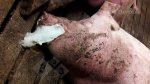
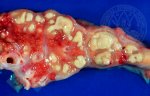
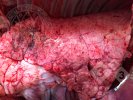
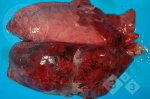
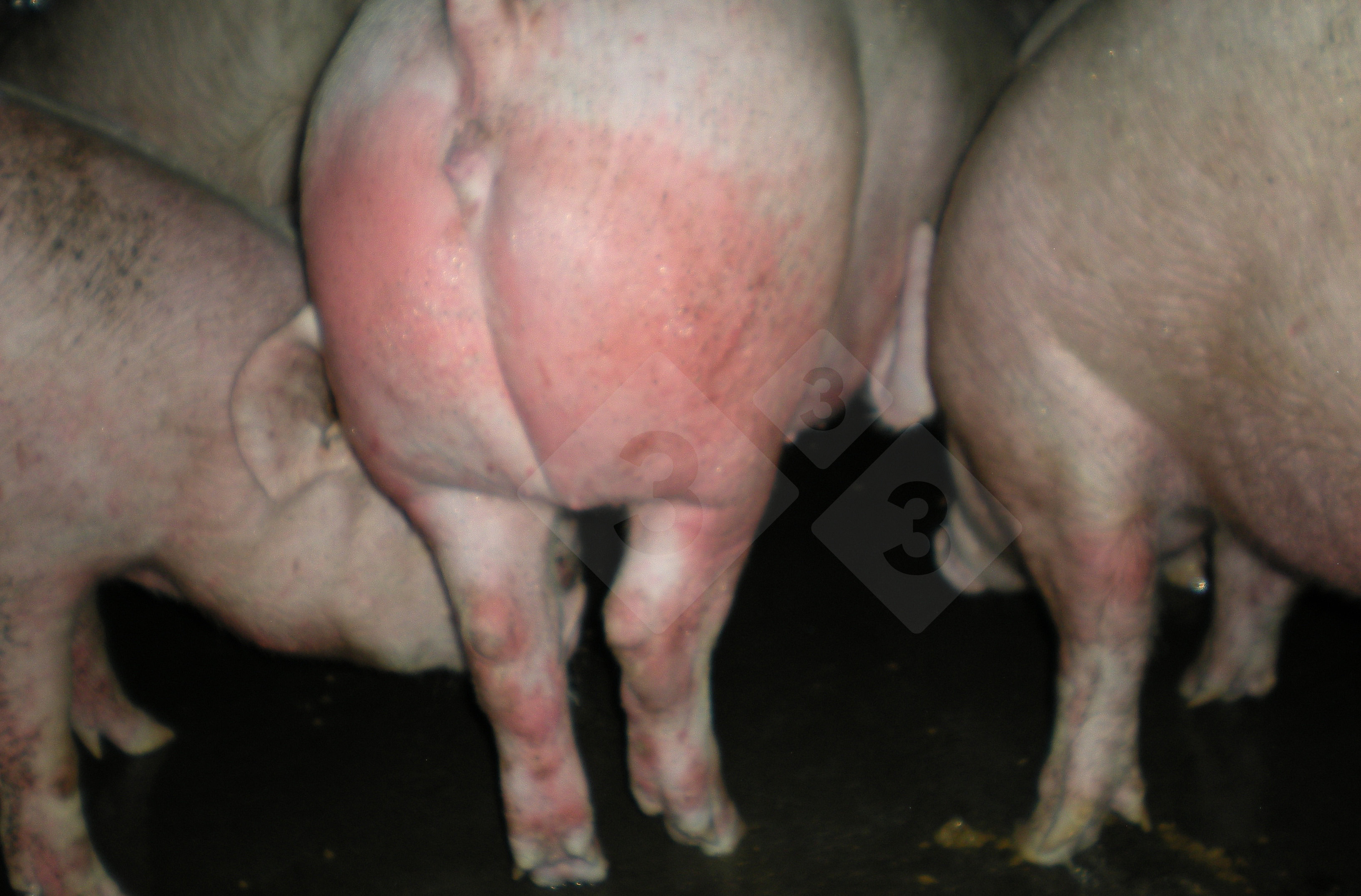
This is scalding of the skin, which occurs when pigs sit for long periods on wet and damp floors soaked with urine, sometimes known as urine scald. Close inspection shows that the skin lesions are a superficial bright red rash on the rear and skin of the back surface of the hind leg hams. It may be exacerbated if there is also some irritant disinfectant also present in the urine and water mixture on the floors. This soaking environment and any minor skin abrasion damage the skin surface to form the visible red congested rash. The situations where pigs are forced to sit in wet urine-soaked floors can include trucks, slaughterhouse holding pens, or in stalls and pens with solid concrete floors, where the drainage is poor and urine accumulates on the floor where the sow is resting. Many disinfectants are strong chemicals that can irritate the skin of pigs. It is therefore important that when disinfectant is used, that it is washed away and the area on the truck or pens is rinsed properly. Other possible causes of this type of condition would include contact allergy reactions and chemical irritation.